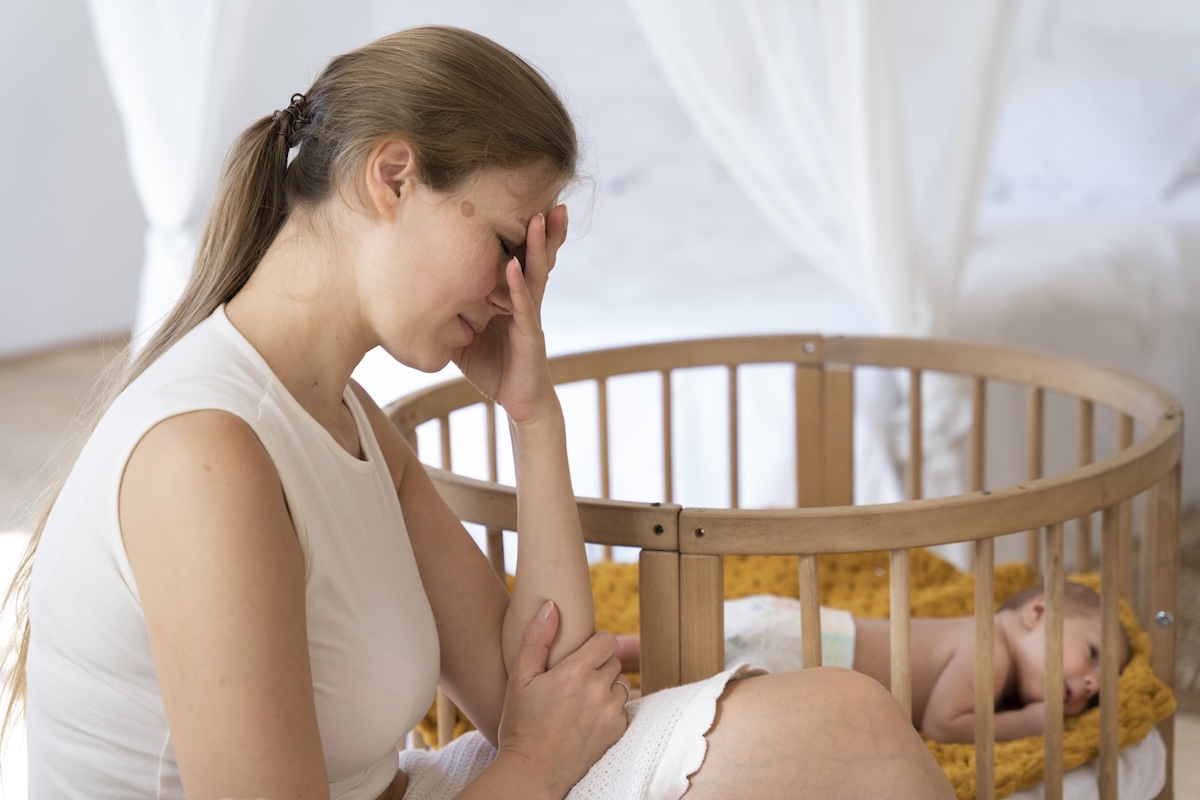
Bringing a new baby into the world is supposed to be one of life’s happiest moments. But for some new moms, it brings unexpected feelings of sadness, fear, or emptiness. This experience is called postpartum depression, and it’s more common than you might think. While it can be scary and confusing, it’s also treatable. Knowing the signs, causes, and options for support can make a big difference.

What Happens After Baby Arrives
Postpartum depression is a mood disorder that affects women after childbirth. It’s not the same as the baby blues, which go away within a week or two. Postpartum depression lasts longer and affects your ability to care for yourself and your baby. It can begin days, weeks, or even months after delivery.
This type of depression can make you feel disconnected from your baby, unsure of your role as a mother, or unable to cope with daily life. It’s important to know that this isn’t your fault. It’s a real medical condition caused by changes in your body and mind.
Possible Causes and Risk Factors for Postpartum Depression
There’s no single cause for postpartum depression. Instead, many things can play a role. One major factor is hormonal changes. After giving birth, your estrogen and progesterone levels drop suddenly, which can impact your mood. At the same time, dealing with a newborn—especially with little sleep or support—can add stress and exhaustion.
Some women are more at risk, such as those with a history of depression, anxiety, or trauma. A difficult pregnancy or delivery, lack of support from a partner, or problems with breastfeeding can also contribute. Even financial stress or having more than one child to care for can make things harder.
There are different forms of postpartum mental health struggles:
-
Mild Depression Or Baby Blues: Common in the first week, usually fades quickly.
-
Postpartum Depression: Longer-lasting sadness and trouble functioning.
-
Postpartum Anxiety Or Panic: Constant worry or fear that something bad will happen.
-
Postpartum Psychosis: A rare but dangerous condition that can cause confusion, hallucinations, or risky behavior.
Continue reading on the next page to discover, among other things, which signs to look out for.